What Is Chronic Inflammation?
Inflammation is your body’s natural response to injury, infection, or harmful stimuli. It’s a protective mechanism designed to promote healing by mobilizing the immune system. There are two types of inflammation:
-
Acute Inflammation: Short-term, localized, and beneficial. For example, swelling and redness after a cut are signs of acute inflammation working to heal the wound.
-
Chronic Inflammation: Long-term and systemic, often harmful. This occurs when the body’s inflammatory response is overactive or fails to turn off, leading to tissue damage and health complications.
Chronic inflammation can persist for months or even years. It’s often subtle, with no obvious symptoms, making it harder to detect. However, it is a key contributor to many chronic diseases, making it essential to understand and manage effectively.
Causes of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation can result from various factors, including lifestyle habits, environmental triggers, and underlying medical conditions.
1. Poor Diet
A diet high in processed foods, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats can trigger inflammation.
-
Inflammatory Foods:
-
Trans fats (found in fried foods and baked goods).
-
Refined carbohydrates (white bread, pastries).
-
Sugary beverages.
-
Processed meats.
-
Why It Happens: These foods can increase levels of pro-inflammatory molecules, such as cytokines, in the body.
2. Stress
Chronic stress elevates cortisol levels, which can dysregulate the immune system and promote inflammation.
-
Impact: Persistent stress puts the body in a constant "fight or flight" mode, delaying the resolution of inflammation.
3. Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity is a significant contributor to chronic inflammation.
-
Why It Matters: Regular exercise helps regulate inflammatory markers and improves circulation, which supports the immune system.
4. Environmental Toxins
Exposure to pollutants, chemicals, and allergens can provoke an inflammatory response.
-
Examples of Triggers: Air pollution, pesticides, and tobacco smoke.
5. Underlying Health Conditions
Certain diseases can perpetuate chronic inflammation, including:
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and lupus involve an overactive immune system attacking healthy tissues.
-
Obesity: Excess fat, particularly visceral fat, produces pro-inflammatory chemicals.
-
Infections: Persistent infections, such as hepatitis or Lyme disease, can drive long-term inflammation.
Symptoms and Effects of Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is often called a "silent killer" because its early symptoms are subtle and easily overlooked. However, it has profound effects on the body over time.
1. Common Symptoms
-
Fatigue
-
Joint pain or stiffness
-
Digestive issues, such as bloating or constipation
-
Skin problems, including redness or rashes
-
Low-grade fever
-
Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
2. Long-Term Effects
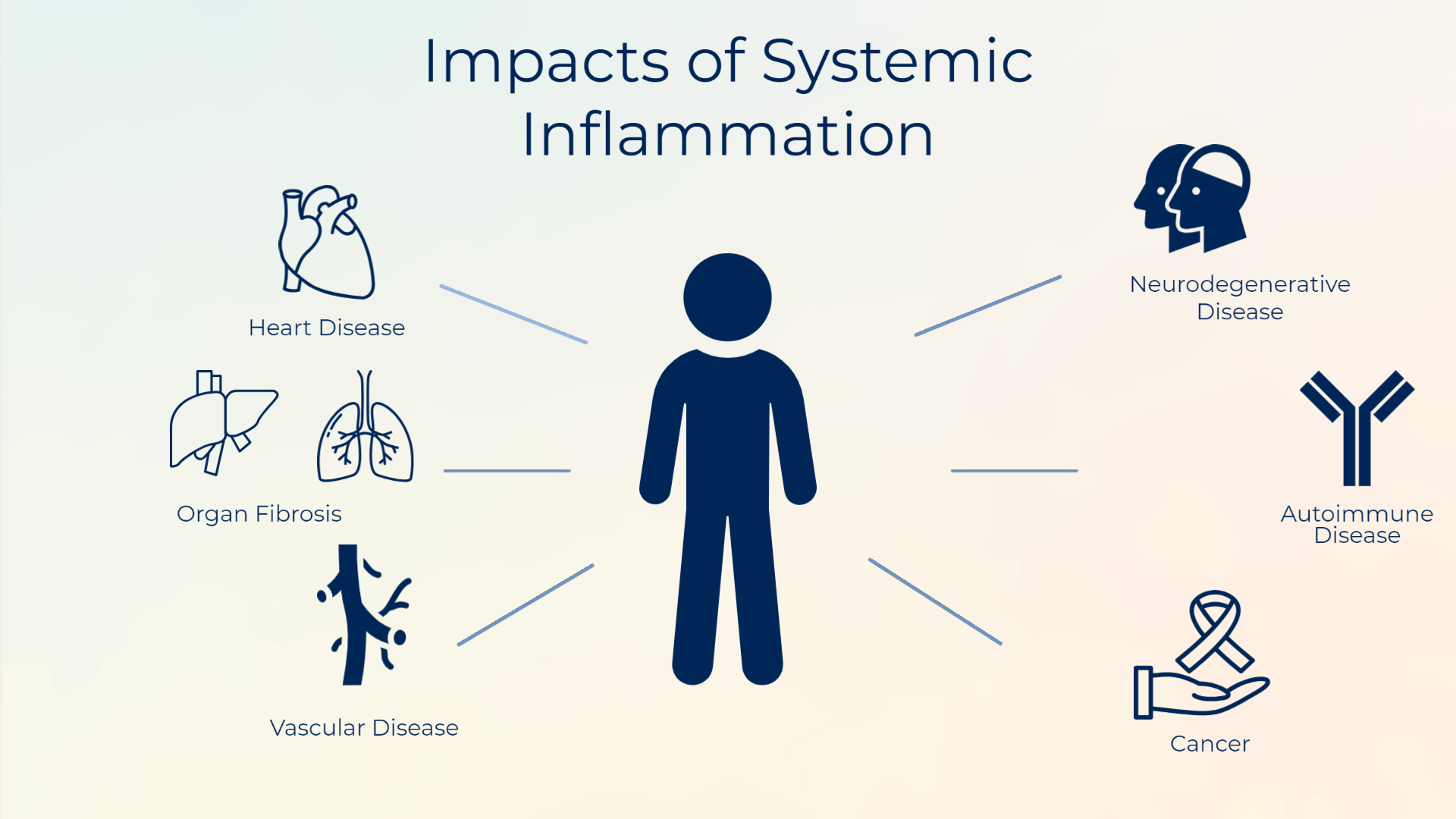
Over time, chronic inflammation can contribute to the development of severe health conditions, such as:
-
Heart Disease: Inflammation can damage blood vessels, leading to plaque buildup and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
-
Type 2 Diabetes: Inflammation interferes with insulin signaling, contributing to insulin resistance.
-
Cancer: Chronic inflammation can trigger changes in cells and promote tumor growth.
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Persistent inflammation can cause the immune system to attack healthy tissues.
-
Neurodegenerative Diseases: Conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s are linked to chronic inflammation in the brain.
Best Ways to Manage and Reduce Chronic Inflammation
Managing chronic inflammation involves a combination of lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and stress management techniques. While there’s no "instant inflammation relief," adopting these strategies can significantly reduce inflammatory markers in the body.
1. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet is one of the most effective ways to reduce chronic inflammation.
Foods to Include:
-
Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants that neutralize free radicals. Examples include berries, spinach, and kale.
-
Healthy Fats: Omega-3 fatty acids in fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) and nuts like walnuts.
-
Whole Grains: Quinoa, brown rice, and oats.
-
Spices: Turmeric and ginger have potent anti-inflammatory properties.
-
Green Tea: Contains polyphenols, which reduce inflammation.
Foods to Avoid:
-
Processed snacks.
-
Sugary drinks.
-
Red and processed meats.
2. Regular Exercise
Engaging in moderate exercise reduces inflammation and improves overall health.
-
Examples: Walking, swimming, yoga, or cycling.
-
Frequency: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress exacerbates inflammation, so adopting stress-relief practices is crucial.
-
Techniques:
-
Mindfulness meditation.
-
Deep breathing exercises.
-
Journaling.
-
Spending time in nature.
4. Adequate Sleep
Poor sleep disrupts the body’s ability to regulate inflammation.
-
Tips for Better Sleep:
-
Establish a consistent sleep schedule.
-
Avoid screens before bed.
-
Create a relaxing bedtime routine.
5. Supplements
Certain supplements can help reduce inflammation, but they should be used under medical supervision.
-
Examples:
-
Omega-3 fish oil.
-
Curcumin (found in turmeric).
-
Probiotics to support gut health.
6. Hydration
Drinking enough water helps flush out toxins and supports the body’s natural healing processes.
Competitor Points: Popular Approaches to Reducing Inflammation
Several products and programs target inflammation management. Here’s a look at some popular approaches:
1. Anti-Inflammatory Diet Plans
Brands like Whole30 and Mediterranean Diet programs promote anti-inflammatory eating.
-
Strengths:
-
Easy to follow with structured meal plans.
-
Backed by scientific evidence.
-
Considerations:
-
May require significant dietary changes.
2. Wellness Apps
Apps like Calm and Headspace offer stress management tools, a critical component of reducing inflammation.
-
Strengths:
-
Convenient and accessible.
-
Encourages mindfulness and relaxation.
-
Considerations:
-
Effectiveness depends on consistent use.
3. Supplement Brands
Companies like Nordic Naturals and Garden of Life offer supplements targeting inflammation, such as omega-3s and curcumin.
-
Strengths:
-
Often supported by clinical studies.
-
Can be integrated into daily routines.
-
Considerations:
-
Should not replace dietary or lifestyle changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is chronic inflammation?
A: Chronic inflammation is a prolonged immune response that can damage tissues and contribute to diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer.
Q: What causes chronic inflammation?
A: Common causes include poor diet, stress, inactivity, environmental toxins, and underlying health conditions like obesity or autoimmune disorders.
Q: How can I reduce inflammation in my body fast?
A: While there’s no instant solution, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress are effective ways to reduce inflammation over time.
Q: Are there supplements that help with inflammation?
A: Yes, omega-3 fish oil, curcumin, and probiotics are some supplements known to reduce inflammation. Consult a healthcare provider before use.
Q: Can chronic inflammation be reversed?
A: Chronic inflammation can often be managed or reduced through lifestyle changes, dietary adjustments, and stress management.
Chronic inflammation is a silent contributor to many health issues, but it’s also manageable with the right strategies. By incorporating an anti-inflammatory diet, regular exercise, and stress-relief techniques into your routine, you can reduce its impact and improve your overall well-being.